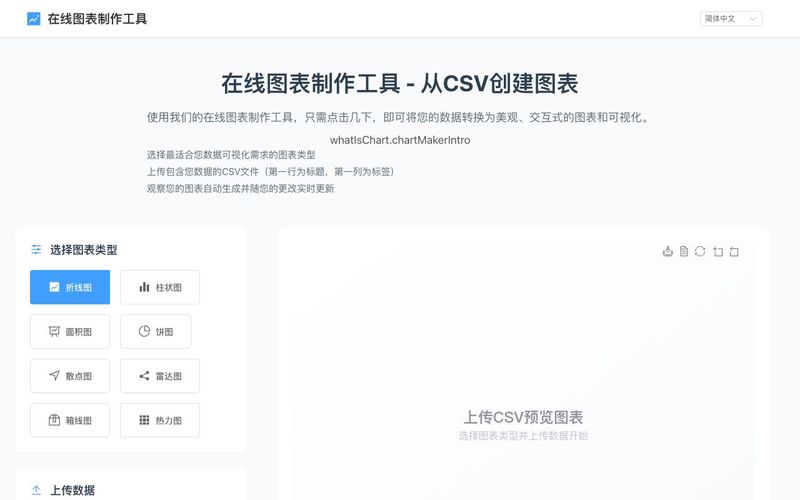
A chart is a graphical representation of data that helps visualize complex information in a simple, understandable format. Charts transform raw numbers and statistics into visual patterns, making it easier to identify trends, comparisons, and relationships within data.
Why Use Charts?
Better Understanding: Visual information is processed 60,000 times faster than text by the human brain
Effective Communication: Charts simplify complex data into clear, digestible visuals
Quick Analysis: Patterns and trends become immediately apparent through visual representation
Professional Presentation: Charts add credibility and professionalism to reports and presentations
Types of Charts and Their Uses
Line Charts
Perfect for showing trends over time and continuous data series. Commonly used for stock prices, temperature changes, and growth metrics.
Bar Charts
Ideal for comparing quantities across categories. Excellent for sales comparisons, survey results, and ranking data.
Pie Charts
Best for showing proportions and percentages of a whole. Great for market share analysis and budget breakdowns.
Scatter Plots
Useful for showing relationships between variables. Often used in scientific research and statistical analysis.
Best Practices for Chart Maker
Choose the Right Type: Select a chart type that best suits your data and message
Keep it Simple: Avoid cluttering your chart with unnecessary elements
Use Clear Labels: Make sure axes, titles, and legends are easily readable
Maintain Consistency: Use consistent colors and styles throughout your charts